The Connection Between Physical Fitness and Mental Health
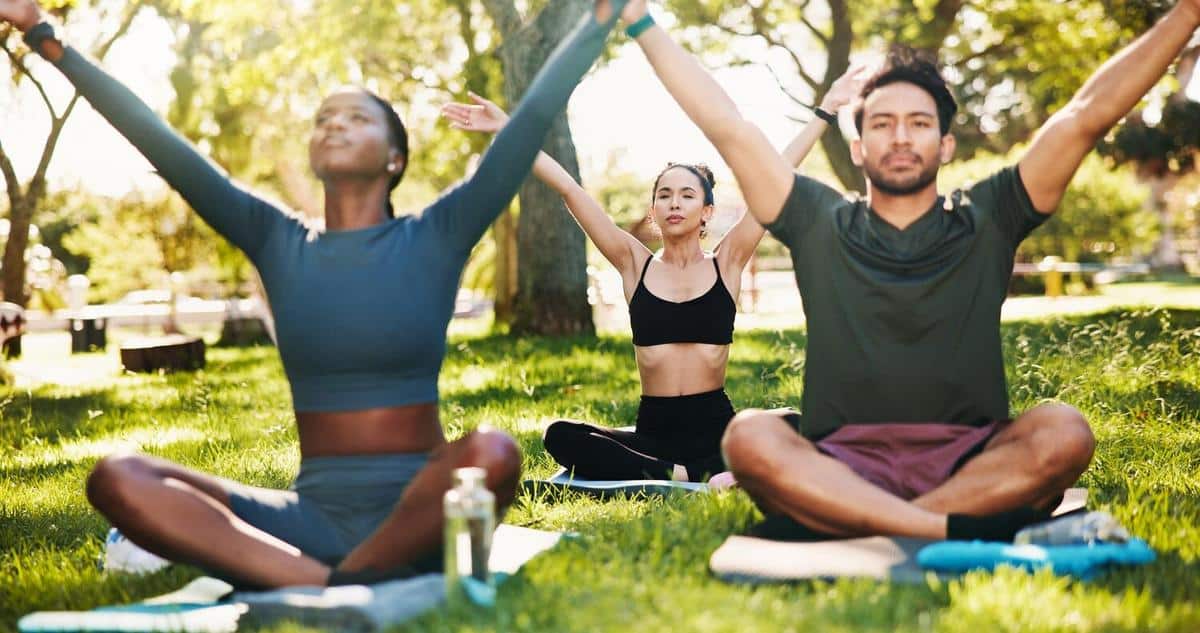
The intricate relationship between physical fitness and mental health has been a subject of growing interest among both researchers and fitness enthusiasts. This connection not only highlights the benefits of a regular exercise routine but also underscores its importance in maintaining mental well-being.
The Synergy Between Body and Mind
Physical fitness is more than just about building muscles or shedding pounds. It’s an essential component of overall well-being that significantly impacts mental health. According to the World Health Organization, regular physical activity can reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, enhancing mood and overall mental health.
Expert Insights
Dr. Samantha Harris, a renowned psychologist, states, “Exercise induces changes in the brain, including neural growth, reduced inflammation, and new activity patterns that promote feelings of calm and well-being.” These changes can have profound effects on mental health, creating a more resilient and positive mindset.
Statistics that Speak Volumes
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that individuals who engaged in regular physical activity were 30% less likely to experience depression. This statistic underscores the powerful influence of exercise on mental health.
Personal Journey: Mark’s Story
Consider Mark, a 40-year-old accountant who struggled with anxiety for years. After incorporating a simple 30-minute walk into his daily routine, he noticed a significant reduction in his anxiety levels. His story is a testament to how even modest exercise can transform mental health.
Actionable Tips for Boosting Mental Health Through Fitness
- Start small: Begin with short sessions and gradually increase the duration and intensity.
- Find something you enjoy: Whether it’s dancing, running, or yoga, choosing an activity you love makes it easier to stick with.
- Set realistic goals: Establish achievable milestones to maintain motivation.
- Incorporate mindfulness: Combine your workouts with mindfulness practices to enhance mental clarity.
To maximize mental health benefits, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week.
Comparing Exercise Types and Their Benefits
| Exercise Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Aerobic Exercise | Improves cardiovascular health and reduces anxiety. |
| Strength Training | Boosts self-esteem and cognitive function. |
| Yoga | Enhances flexibility and reduces stress. |
| Pilates | Improves posture and promotes relaxation. |
| Swimming | Increases endurance and releases endorphins. |
| Cycling | Improves joint mobility and mood. |
| Walking | Boosts energy levels and clarity of thought. |
| Dancing | Encourages creativity and social interaction. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How does exercise affect mental health?
Exercise promotes the release of endorphins and other chemicals that improve mood and reduce stress.
Can exercise replace medication for mental health conditions?
While exercise is beneficial, it should not replace prescribed medication without consulting a healthcare provider.
How often should I exercise to see mental health benefits?
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly for optimal mental health benefits.
Conclusion: Taking the First Step
The connection between physical fitness and mental health is undeniable and profound. By taking small, consistent steps towards incorporating exercise into your daily routine, you can significantly enhance your mental well-being. Embrace the journey towards a healthier mind and body, and enjoy the lasting benefits it brings.